

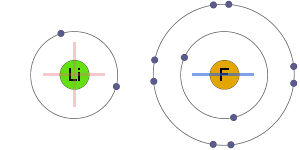
* The Aluminium atom loses 3 electrons and each Fluorine atom gains 1 electron to get their nearest inert gas: Neon's configuration, 2s 22p 6. Note: The electronegativity difference between Mg (1.2) and Cl (3.0) is 1.8. * The electrovalency of Mg is 2 and that of Cl is 1. * Thus formed Mg 2+ and two Cl - ions combine together by forming MgCl 2. * Each Chlorine atom gains one electron to get Argon's configuration, 3s 23p 6. * The Magnesium atom loses two electrons to get Neon's configuration, 2s 22p 6. The formation of ionic bond in this compound can be explained as follows. * The Magnesium chloride is an ionic compound. Note: The electronegativity difference between Li (1.0) and F (4.0) is 3.0, which is greater than 1.7. * The electrovalency of Fluorine is also one since it gains one electron. * The electrovalency of Lithium is one since it loses one electron. * Thus formed Li + and F - ions get attracted towards each other to form the ionic compound LiF. * Whereas, the Fluorine atom gains one electron to get nearest inert gas: Neon's configuration, 1s 22s 22p 6. * In the formation of Lithium fluoride, the Lithium atom loses one electron to get nearest inert gas: Helium's configuration, 1s 2. The electrons in the inner shell are called as core electrons and do not participate in the bond formation.Įlectrovalency: The number of valence electrons either lost or gained by an atom during the ionic bond formation is called electrovalency. These electrons are also called as valence electrons. * Only the electrons in the outer shell participate in bond formation. * Therefore every atom tries to get nearest inert gas configuration either by losing or gaining electrons to form ionic bond. * However, Helium is also highly stable due to 1s 2 configuration. Hence atoms must possess eight electrons in their outer shell to get more stability. * The atoms of inert gases are stable due to octet configuration (ns 2np 6) in their outer shell. The formation of ionic bond was explained by Kossell as follows: KOSSELL'S ELECTRONIC THEORY OF CHEMICAL BONDING * It can be observed that an ionic bond is formed between an electropositive metal atom and an electronegative nonmetal atom. * An ionic bond is formed when the electronegativity difference between two bonding atoms is greater than 1.7 on Pauling's scale. The formation of ionic bond between two atoms can be visualized as follows:
The steps involved in the formation of ionic bond can be summarized as:Ī) An electropositive atom (metal) loses electron(s) to form a positively charged ion called as cation.ī) An electronegative atom accepts the electron(s) to form a negatively charged ion, otherwise known as anion.Ĭ) Thus formed oppositely charged ions come closer to each other due to electrostatic force of attraction and get stability.
ION BONDING FREE
Therefore they can conduct as their ions are free to move.The ionic bond is the electrostatic force of attraction between two oppositely charged ions i.e., a positively charged cation and a negatively charged anion. It is formed due to complete transfer of electrons from one atom to another atom. Ionic compounds dissolve in water easily, when they do this their lattice breaks up completely and water molecules surround the seperated ions. A cube of tightly packed alternate metal and non-metal ions.

This is a regular repeating arrangement of metal and non-metal ions which creates compounds with very high melting points which conduct when molten or in solution but never when solid. Ionic compounds form what is known as a lattice structure. When these two charged particles come together they form an ionic bond because the positive magnesium ion is attracted to the negatively charged chloride ion.
ION BONDING FULL
To become stable it must gain an electron to obtain a full outer energy level. Non-metals form negative ions because they gain electrons to become stable.Ĭhlorine (Cl) has an electron arrangement 2,8,7. They change into ions with a two positive charge. To become stable it must lose its two outer electrons to obtain a full outer energy level.Ītoms are neutral because they have equal numbers of protons and electrons however, when they lose two electrons they are no longer neutral. Magnesium (Mg) has the electron arrangement 2,8,2. Metals form positive ions because they lose electrons to become stable. The ionic bond is the electrostatic force of attraction between a positively charged metal ion and a negatively charged non-metal ion.

Ionic bonds are formed between a metal and non-metal, for example sodium chloride.Īn atom of sodium will lose an electron and form a positive ion.Īn atom of chlorine will gain an electron and form a negative ion. Learn about the basic structure of an ion, related to atomic number and mass.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
